The 12 Branches of Accounting: Their Uses and How They Work Leave a comment

When the company does the work in the following month, no journal entry is recorded, because the transaction will have been recorded in full the prior month. The transaction is recorded as a debit to cash and a credit to unearned revenue, a liability account. When the company earns the revenue next month, it clears the unearned revenue credit and records actual revenue, erasing the debt to cash. Financial accounting guidance dictates when transactions are to be recorded, though there is often little to no flexibility in the amount of cash to be reported per transaction. Forensic accounting involves court and litigation cases, fraud investigation, claims and dispute resolution, and other areas that involve legal matters. As your organization navigates the complexities of today’s dynamic economic environment, a reasonable selection of the accounting branch will align well with your organizational goals.
Small Business Resources
Managerial accounting includes budgeting and forecasting and cost analysis. As well as financial analysis, reviewing past business decisions and more. This is what managers need to make decisions about a business’s operations, not comply strictly with GAAP. Cost accounting is most commonly used in the manufacturing industry, an industry that has a lot of resources and costs to manage. It is a type of accounting used internally to assess a company’s operations.
Internal Focus and Cost Control
Tax accounting also helps businesses figure out their income tax and other taxes and how to legally reduce their amount of tax owing. Tax accounting also analyzes tax-related business decisions and any other issues related to taxes. This branch of accounting helps in handling the state and federal fund allocation and disbursement. It is also called public accounting as it indirectly serves the general public. Government accounting can be including social accounting, a measure of cost humans, climate change, or the proper use and allocation of welfare funds. For example, the reports and records can be analyzed by a financial accountant to check the previous quarter’s performance and make the required changes in the next quarter.
- Under this accounting, the movement of money from various agencies is tracked.
- With this method, bookkeepers debit and credit the cash account in each journal entry, depending on the transaction.
- The unnecessary costs eat up profit and can damage business sustainability.
- The decision will influence your organization’s efficiency, compliance, decision-making, and financial transparency.
- Businesses might look for forensic accountants if they suspect missing assets, fraud, or any other criminal activity involving their business.
The 12 Branches of Accounting: Their Uses and How They Work
In addition, financial statements disclose details concerning economic resources and the claims to those resources. Financial accounting is a type of accounting that records, analyzes, and summarizes business financial transactions. Financial accountants create financial statements and provide information about your business’s financial health and performance to investors, customers, and creditors. Financial accounting is concerned with the preparation of periodic financial reports by using historical data about a business enterprise.
This branch of accounting aids businesses to be compliant with regulations set up by the IRS. This accounting concept helps in improving the administration of the company, enhancing its profit, and providing management with financial reports that leave effects on planning and budgets. Managerial accounting forecasts to advise management on the most profitable business practices so that the required goals can be met. This accounting is useful in conducting internal examinations through Cost to Volume Profit (CVP) or break-even point.
Professional qualifications
For example, the balance sheet reports assets and liabilities while the income statement reports revenues and expenses. Financial accounting is governed by accounting rules and regulations such as U.S. GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) and IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards). Each branch serves distinct purposes and contributes to the financial management of organizations. Financial accounting records, summarizes and reports a company’s business transactions through financial statements.
For example, using information on income, expenses and deductions to calculate taxes owed. This branch of accounting offers information regarding a business’s internal structure, which is management. Unlike in the case of financial accounting, in this area, accountants track the use of money rather than the amount. Since this branch is exclusively for internal purposes, accountants need not follow GAAP. Tax accounting involves planning for tax time and the preparation of tax returns.
With financial accounting, businesses can use both accrual and cash accounting methods to determine net income. It also uses a standard set of rules, called the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), to make reporting consistent across periods and encourage transparency. With global business expansion, international markets and the need for international accounting has also grown. By learning the laws and regulations of other countries, this branch of accounting allows businesses to conduct themselves honestly and fairly. The accounting standard adopted by most global economies, International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), is also followed by international accountants. The preparation of tax returns and planning for tax time are both parts of tax accounting.
It involves adhering to regulations set by tax authorities, ensuring compliance, and optimizing tax strategies. These aspects help minimize the tax burden within the framework of applicable laws. Financial accounting generates detailed reports such as balance sheets and income statements, which help to evaluate a firm’s financial situation. Such reports are crucial for investors, lenders, regulators and other 7 basic invoicing questions you were afraid to ask stakeholders in making decisions on whether or not to get involved with a company. Tax accounting is a distinct field within accounting that involves the management of tax obligations relative to the laws and regulations under the jurisdiction of a tax authority. The goal of tax accounting is to make sure that businesses and individuals compute their tax liability accurately and file their returns on time.
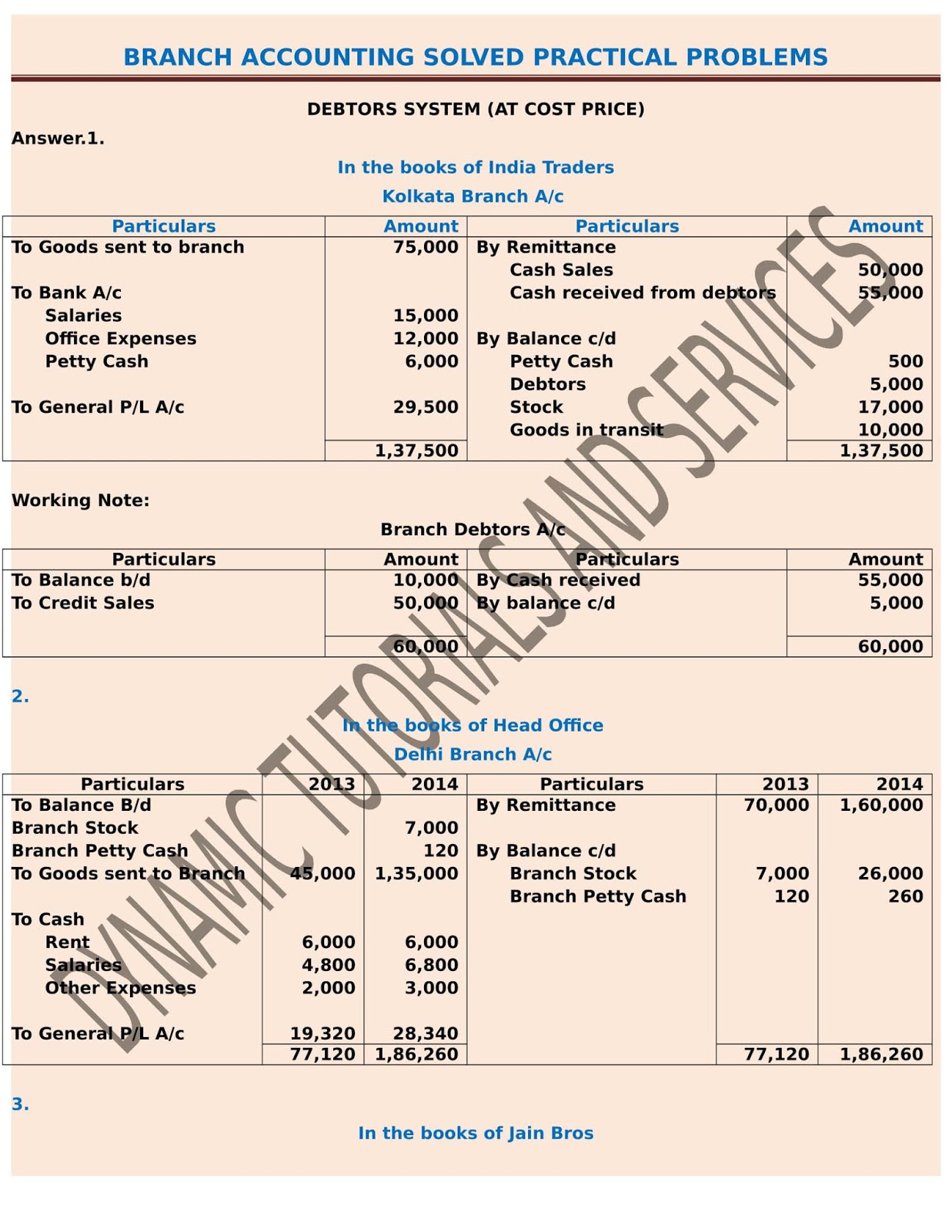
#3 – Head Office Paid Expenses of Branch – If the head office paid wages of $500, rent of $400, and salary of $300 on behalf of the branch. #1 – Inventory – If the head office transferred inventory of $1,000 to its branch office, the journal entries below would be passed into the head office books. Did you know that in the history of accounting, Luca Pacioli is often called the father of accounting? His Summa de Arithmetica, Geometria, Proportioni et Proportionalita, written in 1494, outlined Venetian merchants’ first double-entry bookkeeping system. In the example above, the consulting firm would have recorded $1,000 of consulting revenue when it received the payment. Accountants are ethical guardians responsible for upholding the integrity of financial information.
